Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
(CPR)
1.Make Sure the Scene is Safe
Protection for Yourself, Wear Gloves, Pocket Mask and Protective Glasses
2. Call for the Patient, Check their Response
Tap the patient on the shoulder and ask,
”Are you all right?”. Look for Response.
3. Call for Help
Activate the EMS system, phone 119
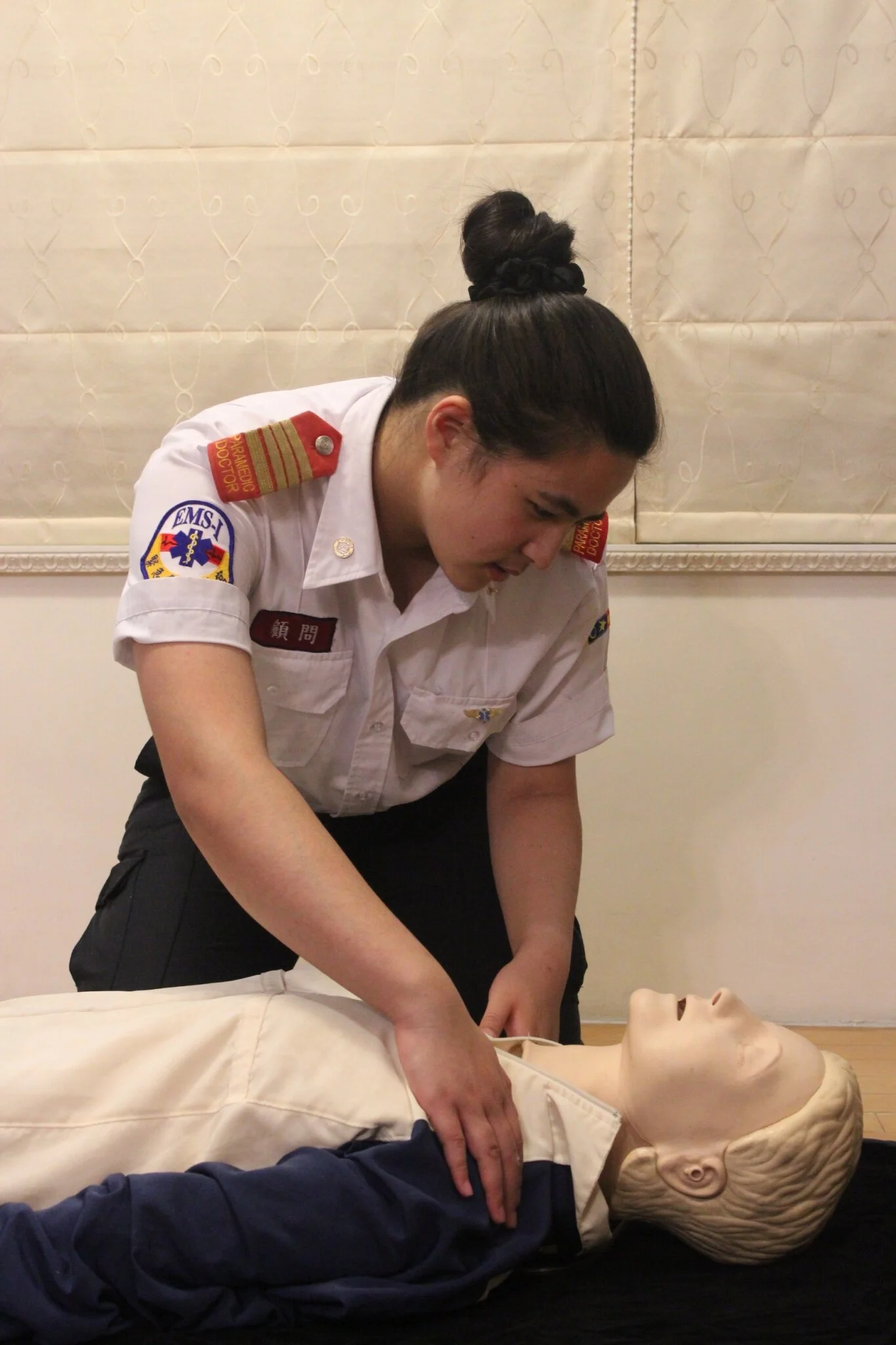
4. Check Breathing
“LOOK” for breathing, detect victim’s with no breathing or only gasps.
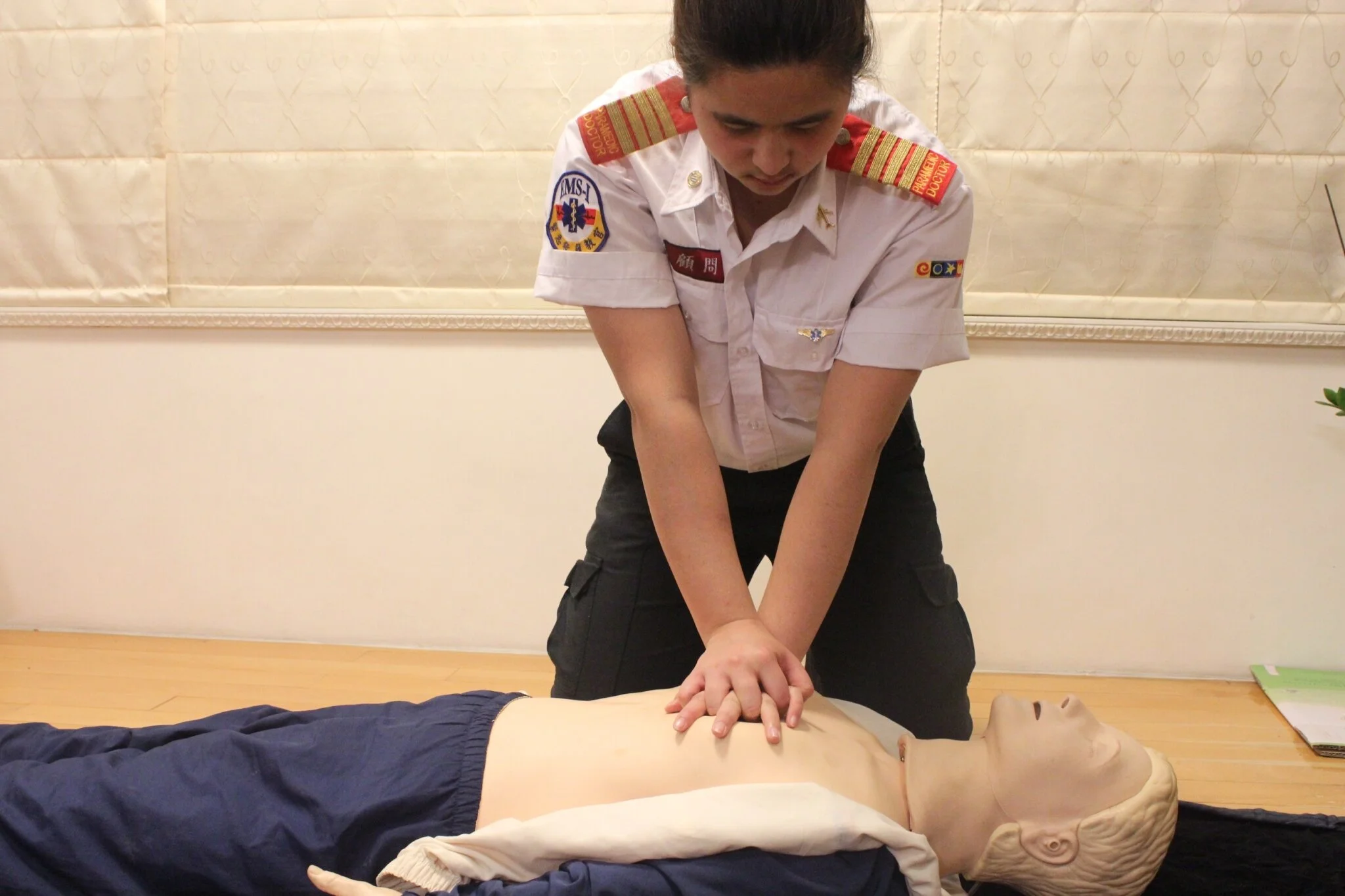
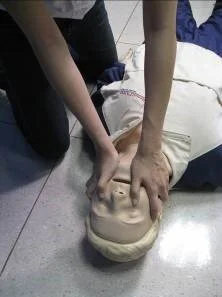
5. Circulation & Compression
If there’s not a sign of breathing or only gasps, call for help then give chest compressions right away. Place one of your hands on the sternum in the center (middle) of the chest between the nipples.
6. Compressions
Then place your other hand on top of the first one so that the hands are overlapped also your both arms must be straight. The compressions and ventilations are at a ratio of 30:2. To perform chest compression at a rate of 100 to 120 per minute, the compression depth for adults has to be more than 5 cm.
For Public
7. Open the Airway
Tilt chin up with index and middle fingers.
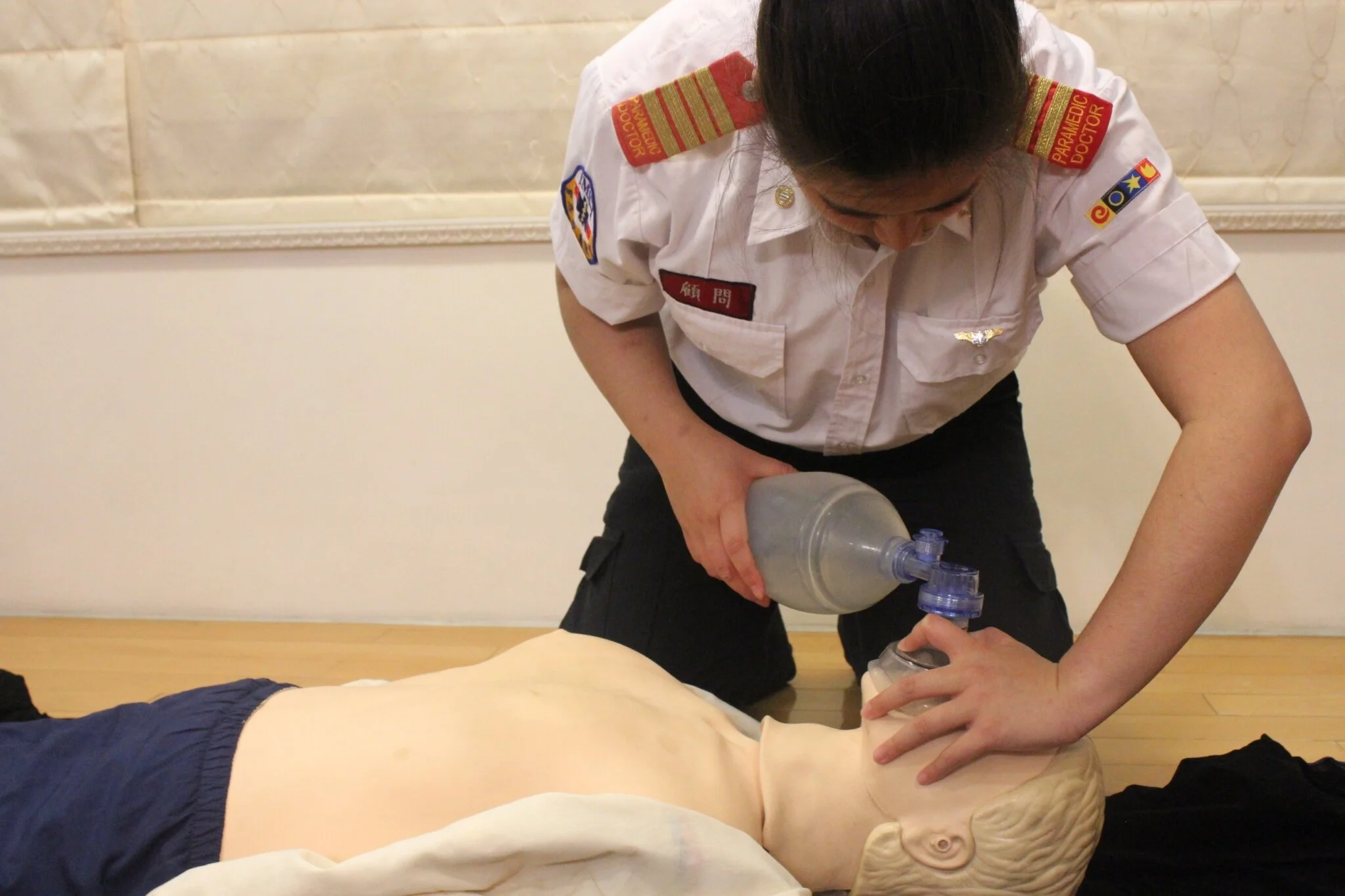
8. Give Breathing
When giving Mouth-to-mouth, pinch the nose with the thumb and index finger. Give 2 Rescue Breaths, each delivered in 1 second so that visible chest rise is produced.
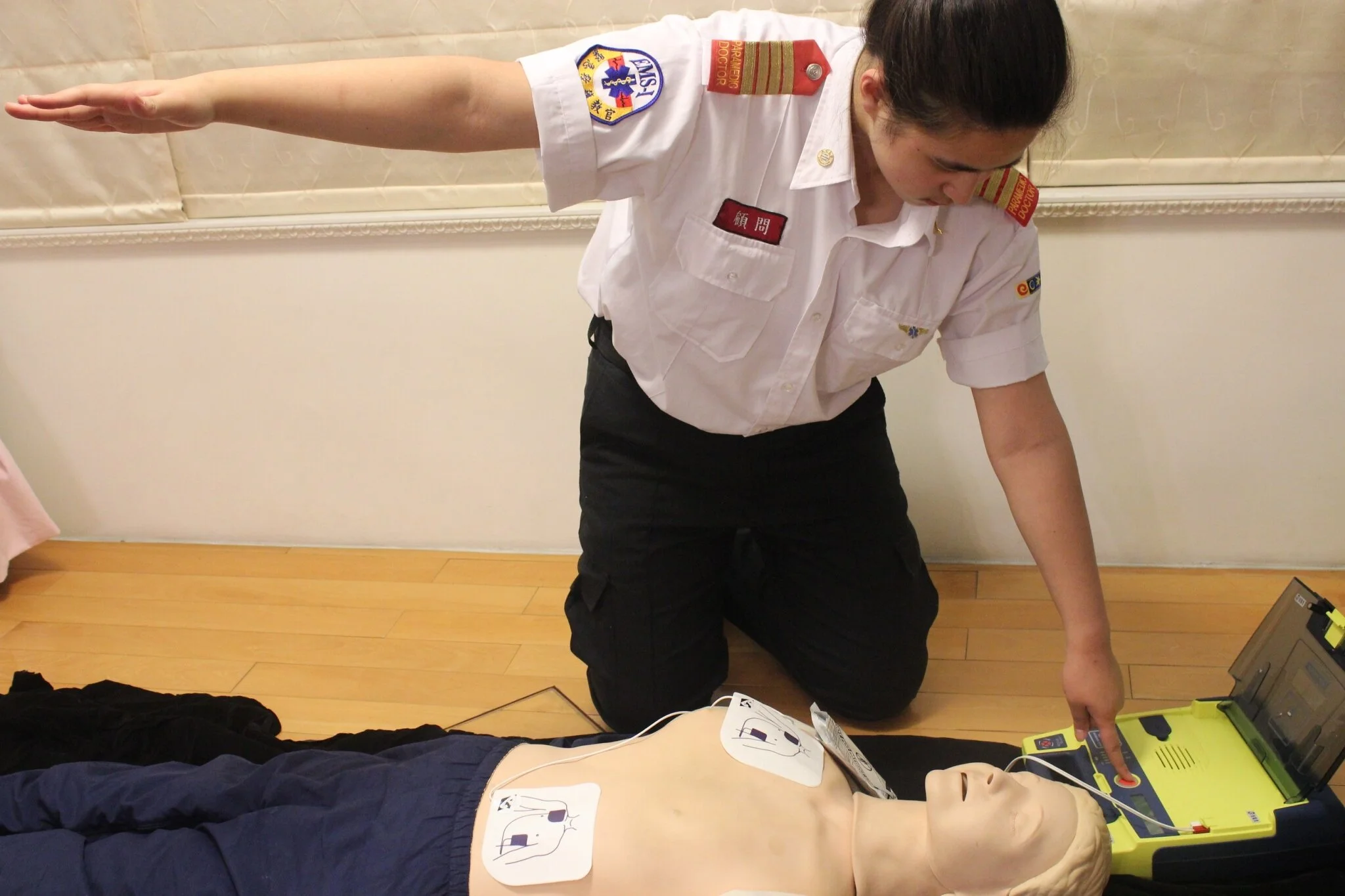
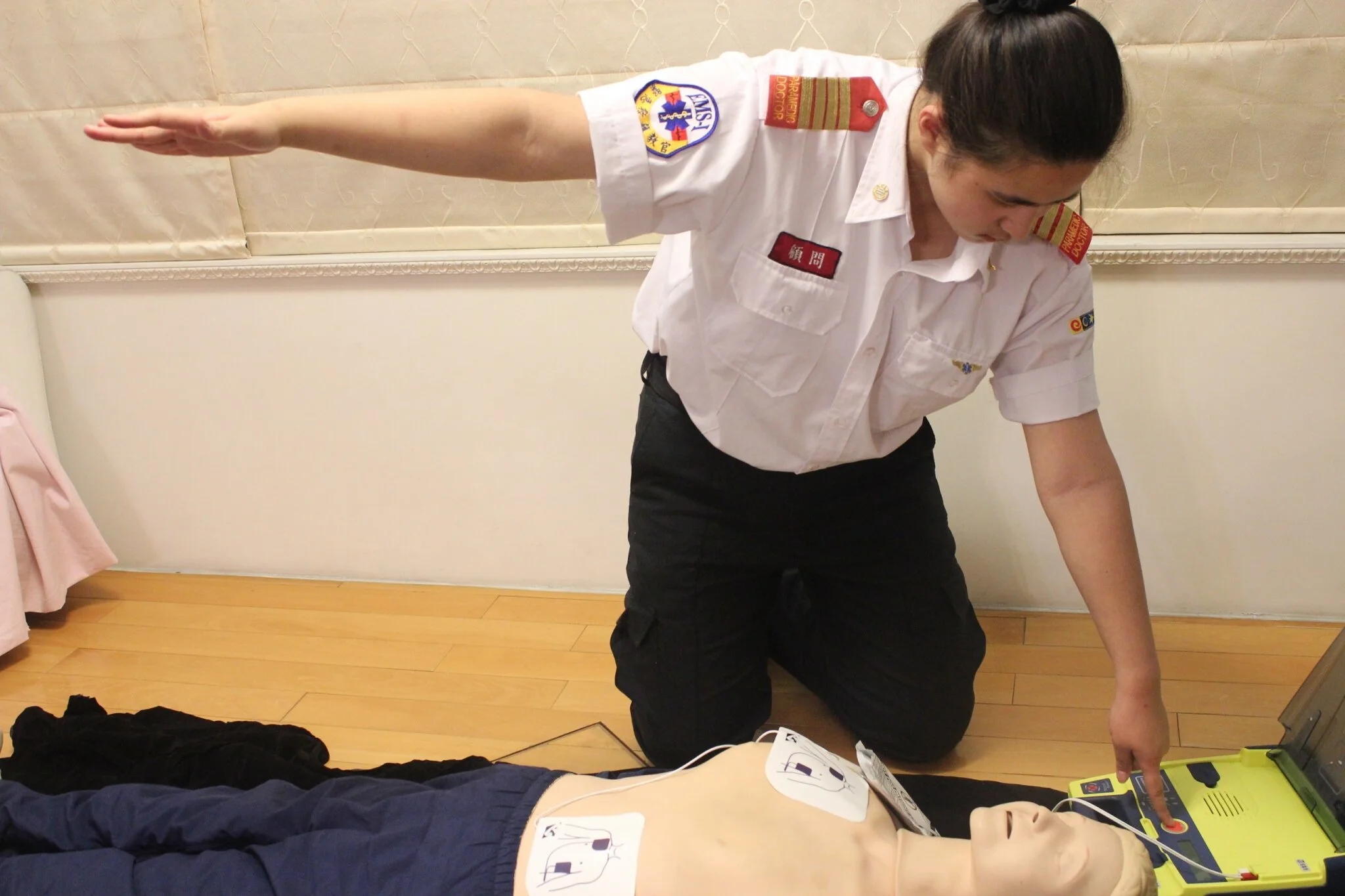
9. AED
Attach the AED to the victim as soon as possible and follow the instructions of the AED.
10. Continue until EMT Arrival
Rescuers should continue compressions and rescue breaths until:
1. An AED(PAD)arrives
2. The victim begins to move
3. A professional responder takes over
For Healthcare Providers
7. Open the Airway
Jaw-Thrust Maneuver (Healthcare Providers Only for traumatic condition)
8. Check Pulse & Breathing
Check Pulse & Breathing, should take no more than 10 seconds to determine the pulse.
9. AED
Attach the AED to the victim as soon as possible and follow the instructions of the AED.
10. Continue Compression & breathing
After 5 cycles of compressions and ventilations at a ratio of 30:2 for every 2 minutes (with either one or two rescuers present), if circulations are still not present, continue with CPR. However if there are spontaneous circulations (palpable pulses or movement) but no breathing can be detected, give rescue breaths at the rate of 10 to 12 breaths per minute, or about 1 breath every 6 seconds until the victim has spontaneous breathing.
Recovery Position
Turn the patient into recovery position, to have better breathing and prevent vomiting